Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Satoru; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
JNC TN8400 2001-005, 41 Pages, 2001/04
A correlation between molecular structure and a vibrational spectrum of interlayer water in Na-smectite was investigated by means of Molecular Dymamics (MDs) simulations. Detailed comparison of simulation results with IR spectroscopic observations for the water-smectite system indicated good agreement. Internal vibrational spectra of water were obtained by the Fourier transformation of velocty auto-correlation function of hydrogen atom. A stretching vibrational spectrum of interlayer water consisted of a broad band with a peak top around 3400cm and a sharp peak around 3650 to 3700cm
and a sharp peak around 3650 to 3700cm . The fomer broad band was assigned to O-H vibrations between water molecules as bulk water, while the latter band was attributed to O-H ones oriented to siloxane surface through hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bond distance, determined as the shortest O-O distance by the radial distribution function (RDF), revealed that hydrogen bond distance between water and siloxane surface (O
. The fomer broad band was assigned to O-H vibrations between water molecules as bulk water, while the latter band was attributed to O-H ones oriented to siloxane surface through hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bond distance, determined as the shortest O-O distance by the radial distribution function (RDF), revealed that hydrogen bond distance between water and siloxane surface (O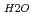 -O
-O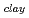
 3.0
3.0  -O
-O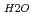 = ca. 2.8 AA ). These results suggested that interaction between water molecule and siloxane surface weaker than that between water molecules, although they were forced to be oriented.
= ca. 2.8 AA ). These results suggested that interaction between water molecule and siloxane surface weaker than that between water molecules, although they were forced to be oriented.